January 14, 2025
What is Packet Loss? How to Test and Fix It?
Have you ever been on an important video call where the audio suddenly cuts out or experienced lag during a critical online gaming session? These frustrating moments often stem from a common networking issue called packet loss. But what exactly is packet loss and how can you address it?
Let’s dive into the details to understand its causes, effects and solutions.
What is Packet Loss?
In simple terms, packet loss occurs when data packets traveling across a network fail to reach their intended destination. These packets are small units of data transmitted over the internet, ensuring seamless communication between devices.
When packets get lost during transmission, it leads to incomplete or delayed information delivery, resulting in noticeable issues like choppy audio, video buffering or even dropped connections.
Effects of Packet Loss on User Experience
Whether you're video conferencing, gaming or transferring files, packet loss can compromise your network performance. Here’s how packet loss affects different scenarios:
1. Increased Latency
When packets are lost, they often need to be retransmitted, leading to delays in communication. This results in higher latency, which causes slow response times in applications and can severely hinder real-time activities like video calls or gaming.
2. Jitter
Unstable packet delivery leads to jitter, where data arrives inconsistently. This is particularly problematic in VoIP calls or video conferences, where uneven delivery causes choppy audio, delayed video and frozen screens.
3. Data Corruption
For applications that rely on complete data, such as file transfers or business operations, packet loss can result in corrupted or incomplete files. Critical data may fail to arrive or arrive in the wrong order, causing files to be unusable or applications to malfunction.
4. Poor User Experience
Packet loss directly degrades the user experience. During streaming, it may lead to buffering or poor video quality. In online gaming, packet loss causes lag, delayed actions, or even disconnects, frustrating players. VoIP services are affected by dropped or distorted audio, making communication difficult.

Additionally, while less noticeable, packet loss can result in slow-loading web pages or interrupted browsing sessions.
5. Disruption in Video Calls and Conferencing
Packet loss during video calls often manifests as audio cutting out, delayed video, or frozen screens, disrupting communication in both personal and professional settings. Effective communication is hindered, leading to frustration and inefficiency in meetings or calls.
6. Lagging Issues in Online Gaming
In competitive gaming, even slight packet loss can ruin the experience, causing lag or delayed actions. Players may also experience sudden disconnects, putting them at a disadvantage during critical moments in a game.

7. Poor Call Quality on VoIP Services
Packet loss on VoIP services leads to poor call quality, with issues like dropped or choppy audio. This makes it difficult to understand or effectively communicate, especially in professional or important conversations.
8. Interruption in File Transfering
When packet loss occurs during file uploads or downloads, it can result in incomplete or corrupted files, leading to failed transfers and productivity delays. Large files may fail to reach their destination entirely, causing significant issues in business operations.
What Are the Causes of Packet Loss?
Several factors can contribute to packet loss, ranging from network congestion to hardware malfunctions. Here are the most common causes:
1. Network Congestion: When too many devices are transmitting data simultaneously, network bandwidth can become overwhelmed, leading to packet loss. This is especially common during peak usage hours.
2. Faulty Network Hardware: Malfunctioning routers, switches, or cables can disrupt the smooth flow of data, causing packets to drop.
3. Software Issues: Outdated or buggy firmware in networking equipment can introduce errors in data transmission, resulting in packet loss.
4. Wireless Interference: For Wi-Fi connections, interference from other devices or obstacles like walls can weaken the signal, increasing the likelihood of packet loss.
5. Cybersecurity Threats: DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) attacks and other malicious activities can overwhelm networks, forcing them to drop packets to manage the load.
6. Configuration Errors: Incorrect network settings or poorly optimized configurations can lead to inefficient data routing and dropped packets.
7. Physical Network Issues: Damaged cables, outdated infrastructure, or poor-quality connections can also contribute to packet loss.
How Can You Detect Packet Loss?
Detecting packet loss is the first step in resolving the issue and ensuring optimal network performance. Testing for packet loss is easy and can help you understand if your internet connection is causing the problem.
Below are some effective methods you can use to identify packet loss and understand its impact on your connection:
Method 1: Using Command Prompt
This method works on both Windows 10 and 11 and requires just a few simple steps.
Here’s how you can test for packet loss on a Windows PC:
Step 1: Open Command Prompt
First, you’ll need to open the Command Prompt on your PC. It’s a tool that allows you to enter commands directly into your computer.
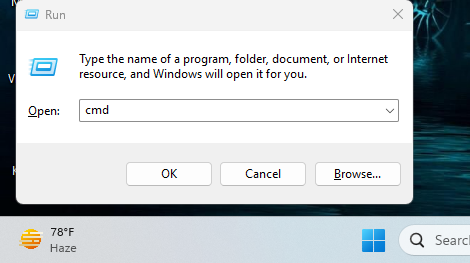
- Press the Windows key + R at the same time to open the “Run” box.
- Type cmd in the box and press Enter or click OK. This will open the Command Prompt window.
Step 2: Enter the Ping Command
Now that the Command Prompt is open, you’ll need to type a special command to test for packet loss. Here's what to do:
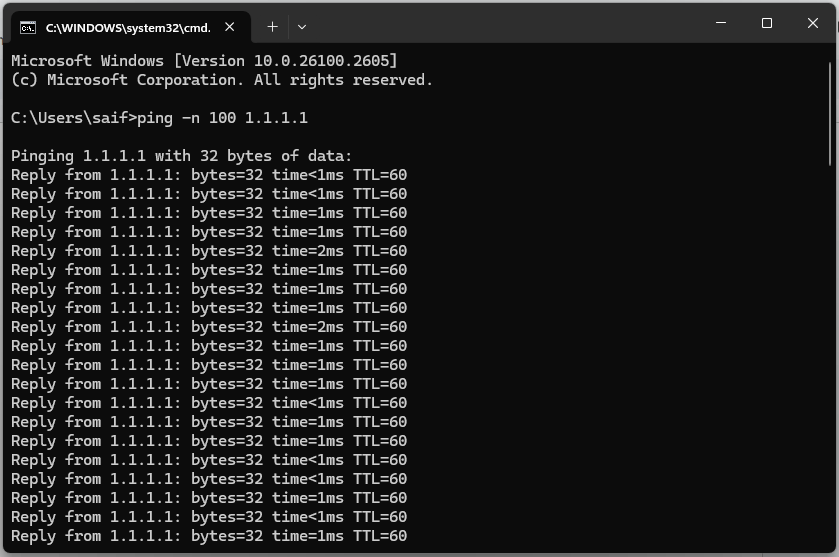
1. In the Command Prompt window, type this command: ping -n 100 1.1.1.1
- ping sends a signal to a server to check your connection.
- -n 100 tells the test to send 100 signals.
- 1.1.1.1 is the IP address for Cloudflare’s DNS server, which is a fast and reliable server for testing your connection.
2. Press Enter to start the test
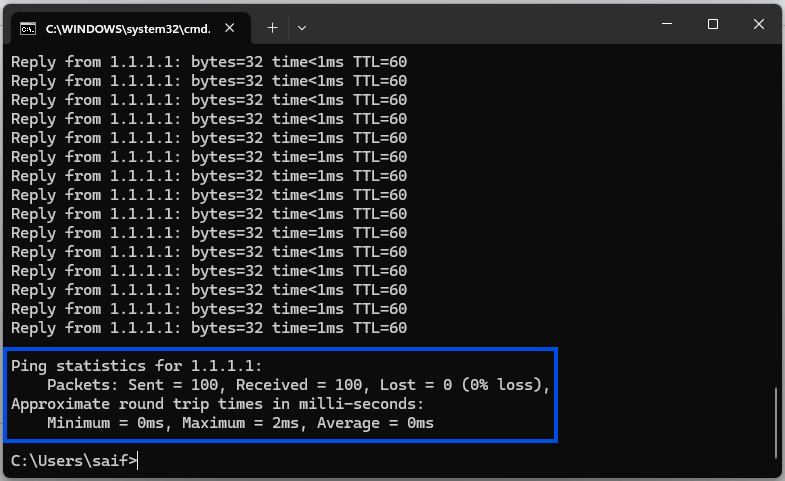
Step 3: Check the Results
After a few seconds, the test will complete and you’ll see a summary of the results. The summary will show the number of packets sent and the number of packets that were lost during the test.
Method 2: Online Tools with Packet Loss Detection
Many online speed test platforms now include packet loss analysis as part of their diagnostics.
How They Work:
- These tools simulate data transmission to servers and analyze how many packets fail to reach their destination.
- Websites like Packetlosstest.com allow you to quickly assess packet loss alongside download and upload speeds.
Using such tools can give you a quick, non-technical way to detect packet loss.
Method 3: Observe Real-Time Symptoms
Even without tools, packet loss often manifests in noticeable ways:
- Video calls with distorted audio or frozen screens.
- Lag or stutter in online gaming.
- Delayed or failed file downloads.
These symptoms provide clues to underlying network issues, including packet loss.
Understanding Packet Loss Test Results
When testing for packet loss, you’re checking if any data is missing while traveling across the internet. The test sends small data packets to a server and waits for a response. If the packet reaches its destination, it counts as a successful ping. For accuracy, at least 50 pings are sent.
For example, if you send 100 pings and get only 99 responses, it means 1% of the data was lost.
Generally, a packet loss of 1% or less is considered acceptable and your online activities should not be affected. However, if packet loss exceeds 5%, you may notice slow website loading, buffering videos, or issues during video calls.
For an optimal internet experience, especially for important tasks like work or gaming, keeping packet loss below 1% is ideal. Anything higher could indicate a problem worth addressing to avoid poor internet performance.
How to Fix Packet Loss?
Addressing packet loss requires tackling the root causes and employing both basic troubleshooting and advanced solutions. Here’s a comprehensive guide:
1. Reduce Network Congestion
- Disconnect unused devices from your network to free up bandwidth.
- Close background applications such as automatic updates, streaming services, or downloads that may consume network resources.
- Schedule bandwidth-heavy activities during off-peak hours to minimize strain.
- Upgrade your internet plan if your household or office consistently faces congestion during high-usage periods.
2. Update Network Hardware
- Ensure your router and modem have the latest firmware updates. You can do this by accessing your router’s settings (refer to the manual or manufacturer’s website for instructions).
- Replace outdated or damaged hardware like old routers, modems, or Ethernet switches to improve reliability and reduce packet loss.
- If your current hardware isn’t meeting your needs, consider investing in modern routers supporting Wi-Fi 6 or advanced Ethernet switches.
3. Optimize Wi-Fi Signal
- Place your router in a central, unobstructed location for even signal distribution. Avoid walls, metal objects, or appliances that can cause interference.
- Use a mesh network system to eliminate Wi-Fi dead zones and improve coverage throughout your home or office.
- Switch to a wired Ethernet connection for high-priority tasks like gaming, video conferencing, or streaming, as it eliminates interference common with wireless networks.
- If using Wi-Fi, upgrading to a Wi-Fi 6 router ensures better performance under heavy load.
4. Check for Malware or Attacks
- Run a comprehensive malware scan using trusted antivirus software on all connected devices. Malware can consume bandwidth and increase packet loss.
- Install security measures like firewalls to protect against DDoS attacks and mitigate other network vulnerabilities.
- Regularly update security software to defend against emerging threats.
5. Reconfigure Network Settings
- Reset your router to factory settings if you suspect misconfigurations. This can often resolve untraceable issues.
- Optimize MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) settings. This determines the size of data packets sent over your network. An improperly configured MTU can lead to fragmentation and packet loss.
- Activate Quality of Service (QoS) in your router settings to prioritize critical applications like gaming or VoIP while minimizing bandwidth for less demanding activities like web browsing.
6. Replace Faulty Cables and Ports
- Inspect ethernet cables for damage such as cuts, bends, or wear. Replace them with high-quality options like Cat 6 cables for reliable connections.
- Switch the Ethernet cable to a different port on the router to rule out issues with faulty ports.
7. Consider a Dedicated Internet Connection for Businesses
Businesses often experience packet loss due to shared bandwidth in standard connections. Upgrading to a dedicated internet connection ensures stable, high-speed access by eliminating the competition for resources with other users.
This is particularly beneficial for activities like video conferencing, VoIP, and managing critical applications.
Final Thoughts
Packet loss can disrupt your online activities, but understanding its causes and knowing how to detect and fix it can make a significant difference. Whether it’s updating hardware, reducing congestion, or reconfiguring settings, addressing packet loss helps ensure a smoother and more reliable network experience.
By staying proactive and implementing preventive measures, you can minimize packet loss and enjoy uninterrupted connectivity for work, gaming or entertainment.